Bottomland hardwood forests blh are found in temperate humid regions of the southeastern us primarily on alluvial floodplains adjacent to rivers.
Bottomland hardwood forest characteristics.
Bottomland hardwood forests typically have distinct ecological zones at different elevations and flood frequencies.
The soil which erodes from the bank is often deposited on the inside bend downstream on what is referred to as a point bar.
They are generally found along the edges of lakes and rivers and in sinkholes.
1 common characteristics of bottomland swamp forests in the south atlantic coastal plain hydrology effects species composition o persistent.
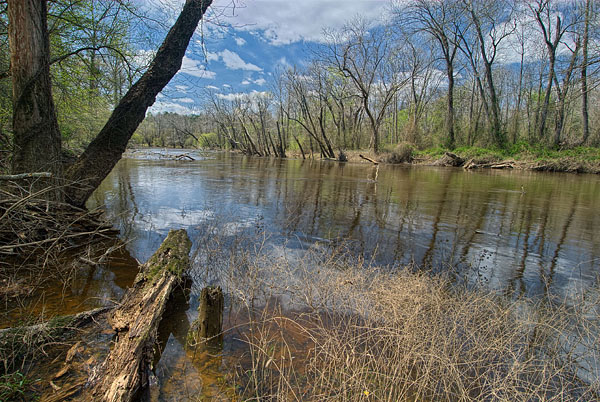
The bottomland hardwood forest is a type of deciduous and evergreen hardwood forest found in us broad lowland floodplains along large rivers and lakes.
Our objective was to characterize the vegetative composition and abundance in a bottomland hardwood stand which had been under an annual flooding regime for over 50 years.
Results indicate that overcup oak is dominant in all three vertical layers while the more desirable willow oak is common only in the overstory.
Patrick jr j george dissmeyer 2 donai d.
They are occasionally flooded which builds up the alluvial soils required for the gum oak and bald cypress trees that typically grow in this type of biome.
Hook 3 victor w.
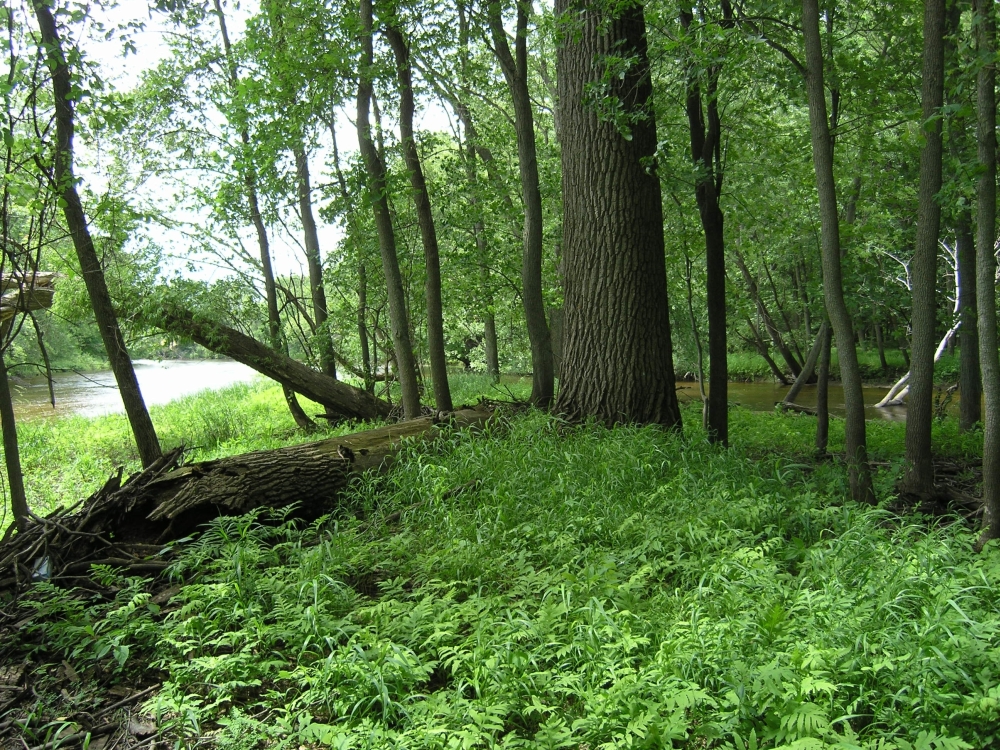
Bottomland hardwood forests support a great variety of tree and shrub species.
Typical tree species growing in these forests range from cottonwoods and sweetgums to cherrybark oaks water oaks and hickories.
276 characteristics of wetlands ecosystems of southeastern bottomland hardwood forests william h.
Bottomland swamp forest silviculture symposium field tour.
Bottomland hardwood forests can reduce the risk and severity of flooding to downstream communities by providing areas to store floodwater.
Bottomland forests represent a transition between drier upland hardwood forest and very wet river floodplain and wetland forests.
Historic blhs were a product of the natural hydrologic and geomorphic processes associated with their adjacent rivers.
These zones are the result of an active river cutting its banks and forming new land putnam 1960.
You can use the term bottomland forest loosely to refer to a variety of wooded habitats but true bottomland forests have these characteristics.
They are seasonally wet areas for example from annual spring flooding.